UUM BEEB 1013 Principles of Economics
Chapter 20: Introduction to Macroeconomics
20.1 Macroeconomic
Concerns
Output Growth
1) Business cycle (Kitaran Perniagaan / 经济循环) : The cycle of short-term
ups and downs in the economy.
2) Aggregate output (Keluaran agregat / 总合产量) : The total quantity of goods
and services produced in an economy
in a given period.
Figure 1: A Typical Business Cycle
1. Expansion or boom (Pengembangan ekonomi / 经济繁荣期): The period in the
business cycle from a trough up to a peak during which output
and employment grow.
Example: The economy is expanding as it moves through point A
from the trough to the peak.
2. Recession / Contraction / Slump (Kemerosotan
ekonomi / 经济衰退期): A period during which aggregate output declines.
Conventionally, a period in which aggregate output declines for two consecutive
quarters. The period in the business cycle from
a peak down to a trough during
which output and employment fall.
Example: The economy is in recession when it moves through point B from
a peak down to a trough.
3.
Depression (Kemelesetan ekonomi / 经济萧条期): A prolonged and deep
recession
Example: The economy is
in depression when it is at trough point.
4. Recovery (Pemulihan ekonomi / 经济复苏期): The period in the business
cycle from a trough up to a peak during
which output and employment grow again
Example:
The economy is in recovery when it raises up again from the trough to the peak.
Economy in Reality (US Economy)
Figure 2: U.S. Aggregate Output (Real GDP), 1900–2009
Unemployment
1) Unemployment rate:
The percentage of the labor force that is unemployed.
Kadar pengangguran 失业率: Satu ukuran yang menunjukkan peratusan jumlah tenaga buruh yang tidak melakukan sebarang kegiatan
ekonomi berbanding dengan jumlah tenaga buruh di pasaran.
Inflation and
Deflation
1) Inflation: An increase in
the overall price level of goods and services.
Inflasi
通货膨胀: Satu keadaan yang menunjukkan kenaikan tingkat harga umum barang dan perkhidmatan secara berterusan.
2) Hyperinflation: A
period of very rapid increases in the overall price level of goods and services.
Hiperinflasi
恶性通货膨胀: Satu proses kenaikan tingkat harga umum barang dan perkhidmatan secara
berterusan dan melampau pada kadar yang sangat
tinggi (> 10%).
3) Deflation: A decrease in
the overall price level of goods and services.
Deflasi
通货紧缩:Satu
proses penurunan tingkat harga umum barang dan perkhidmatan secara berterusan.
20.2 The
Components of the Macroeconomy
To see the big
picture, it is helpful to divide the participants in the economy into four
broad groups:
(1)
Households (Isi Rumah / 家庭成员)
(2)
Firms (Firma / 商家)
(3)
The government (Kerajaan / 政府)
(4)
The rest of the world (Sektor Luar Negara / 外国机构)
Households and
firms make up the private sector, the government is the public sector, and the
rest of the world is the foreign sector.
The Circular
Flow Diagram
1) Circular flow: A diagram showing the income
received and payments made by
each sector of the economy.
2) Transfer payments: Cash
payments
made by the government to people who do not supply goods, services, or labor in exchange for these payments. They include social security
benefits, veterans’ benefits, and welfare payments.
Circular flow
(English version) :
Figure
3: Circular Flow Diagram 1
·
Households receive income from firms and the government, purchase goods
and services from firms, and pay taxes to the government.
·
They also purchase foreign-made goods and services (imports).
·
Firms receive payments from households and the government for goods and
services; they pay wages, dividends, interest, and rents to households and
taxes to the government.
·
The government receives taxes from firms and households, pays firms and
households for goods and services—including wages to government workers—and
pays interest and transfers to households.
·
Finally, people in other countries purchase goods and services produced
domestically (exports).
Note: Although not shown in this diagram, firms and governments also purchase
imports.
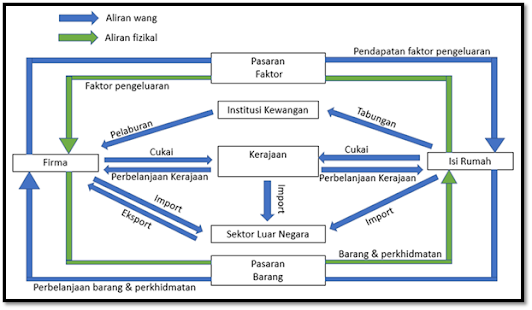
Circular flow (Malay
version) :
Figure
4: Circular Flow Diagram 2
1) Isi Rumah (家庭成员)
·
Menerima pendapatan dalam bentuk upah, sewa, kadar bunga atau untung
daripada firma dan kerajaan
·
Membelanjakan pendapatannya untuk membeli barang dan perkhidmatan yang
dikeluarkan oleh firma
·
Menabung baki pendapatan yang tidak dibelanjakan di institusi kewangan
·
Membayar cukai (seperti cukai pendapatan perseorangan) kepada kerajaan
·
Mengimport barang dan perkhidmatan dari luar negara
2) Firma (商家)
·
Membayar pendapatan faktor kepada isi rumah atas penggunaan faktor
pengeluarannya
·
Memperoleh pendapatan / hasil jualan daripada isi rumah dan kerajaan
·
Membayar cukai (seperti cukai keuntungan syarikat) kepada kerajaan
·
Membuat pinjaman dan pelaburan daripada institusi kewangan
·
Mengimport barang modal, barang perantaraan dan bahan mentah dari luar
negara
·
Mengeksport barang dan perkhidmatan ke luar negara
3) Kerajaan(政府)
·
Memungut cukai pendapatan perseorangan daripada isi rumah dan cukai
keuntungan syarikat daripada firma
·
Melakukan perbelanjaan kerajaan (seperti membeli barang dan perkhidmatan
yang dikeluarkan oleh firma dan memberikan bayaran pindahan dan subsidi kepada
isi rumah)
·
Mengimport barang modal dan kelengkapan pertahanan awam dari luar negara
The Major Economic Goals
1) Price Stability (Kestabilan tingkat harga umum 市场价钱稳定)
We need to understand how to measure prices to control
price stability to avoid inflation issue
2) Low Unemployment (Kadar pengangguran yang rendah 低失业率)
We need to know how to measure unemployment
3) High and Sustained Economic Growth (Meningkatkan
pertumbuhan ekonomi 提升经济成长率)
We need to know how to measure economic growth – which
takes us to a discussion of nominal GDP and Real GDP
U may refer the previous notes in malay version:
https://jlcy2020.blogspot.com/2020/04/bab-1-pengenalan-kepada-makroekonomi.html?m=1
The Three
Market Arenas
1) Another way of
looking at the way households, firms, the government, and the rest of the world
relate to one another is to consider the markets in which they interact.
2) We divide the
markets into three broad arenas:
(1)
The goods-and-services market.
(2)
The labor market.
(3)
The money (financial) market.
Goods-and-Services
Market
·
Households and
the government purchase goods and services from
firms in the goods-and-services
market.
·
Firms purchase goods and services from each other and also
supply to the goods-and-services market.
·
Households,
the government, and firms demand from
this market.
·
The rest of the world buys from and sells to the
goods-and-services market.
Labor Market
·
In
the labor market, households supply labor
and firms and the government demand labor.
·
Labor
is also supplied to and demanded from the
rest of the world.
Money Market
·
Households supply funds to the money market—sometimes called the financial market—in the
expectation of earning income in the form of dividends on stocks and interest
on bonds.
·
Households
also demand (borrow) funds from this market to finance various purchases.
·
Firms borrow to build new facilities in the hope of earning more in the future.
·
The government borrows by issuing bonds.
·
The rest of the world borrows from and lends to
the money market.
·
Much
of this borrowing and lending is coordinated by financial institutions, which
take deposits from one group and lend them to others.
Monetary Terms
·
Treasury bonds, notes, and bills: Promissory notes issued by the federal government
when it borrows money.
Bil-bil perbendaharaan
dan bon kerajaan: Nota janji atau sekuriti hutang yang
dikeluarkan oleh kerajaan pusat
apabila mereka ingin meminjam wang.
·
Corporate bonds:
Promissory notes issued by firms
when they borrow money.
Bon korporat:
Nota janji atau sekuriti yang
dikeluarkan oleh firma semasa mereka meminjam wang.
·
Shares of stock:
Financial instruments that give to
the holder a share in the firm’s ownership and therefore the
right to share in the firm’s profits.
Saham:
Sekuriti yang mewakili sebahagian modal pemilik dalam perniagaan dan pemegang saham juga
merupakan pemilik perniagaan dan mempunyai hak
untuk berkongsi keuntungan atau kerugian sesebuah perniagaan.
·
Dividends:
The portion of a firm’s profits that the firm pays
out each period to its shareholders.
Dividen:
Bahagian keuntungan syarikat yang dibayar
oleh syarikat kepada pemegang sahamnya pada setiap tempoh.
The Role of
the Government in the Macroeconomy
1) Fiscal policy (财政政策):
Government policies concerning taxes and
spending.
Dasar
fiskal: Tindakan kerajaan mengubah perbelanjaan
kerajaan dan cukai untuk menstabilkan
keadaan ekonomi negara.
2) Monetary policy (货币政策): The tools used by the
Federal Reserve to control the short-term
interest rate.
Dasar
kewangan: Tindakan bank pusat mengawal penawaran wang dan kadar bunga dalam ekonomi untuk menstabilkan keadaan ekonomi
negara.
20.3 A Brief
History of Macroeconomics in US
1) Great Depression: The period of severe economic contraction and high
unemployment that began in 1929 and continued throughout the 1930s.
2) fine-tuning: The phrase used by Walter Heller to refer to the
government’s role in regulating inflation and unemployment.
3) stagflation: A situation of both high inflation and high
unemployment.